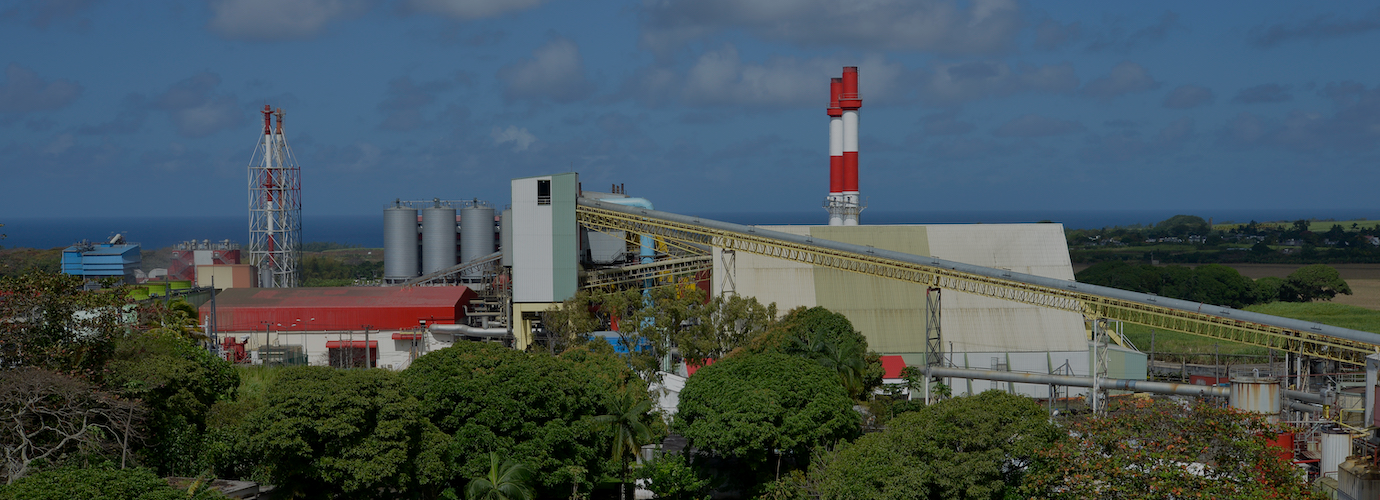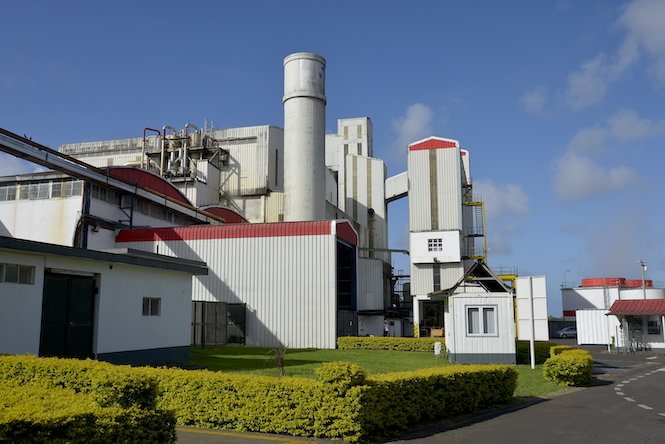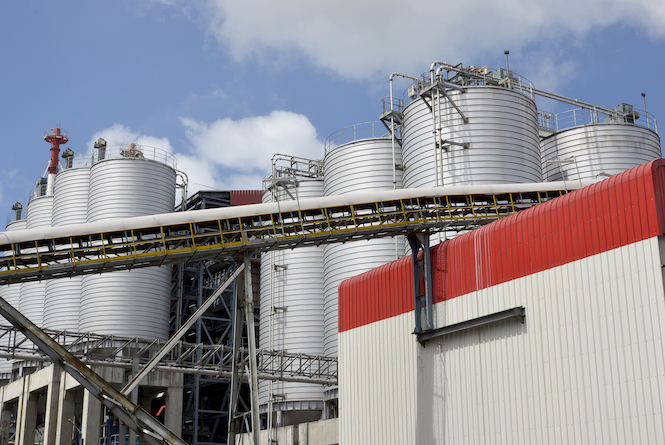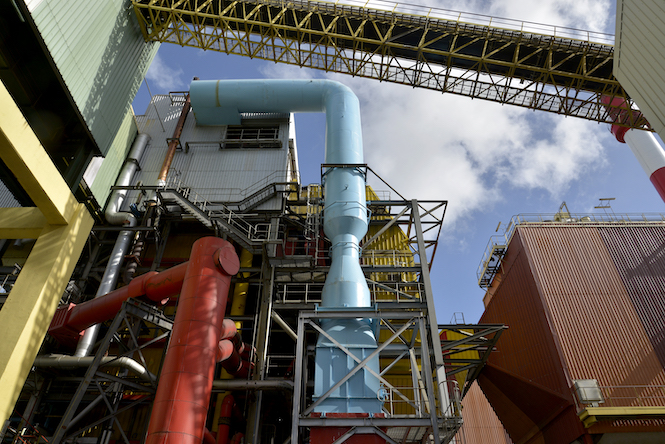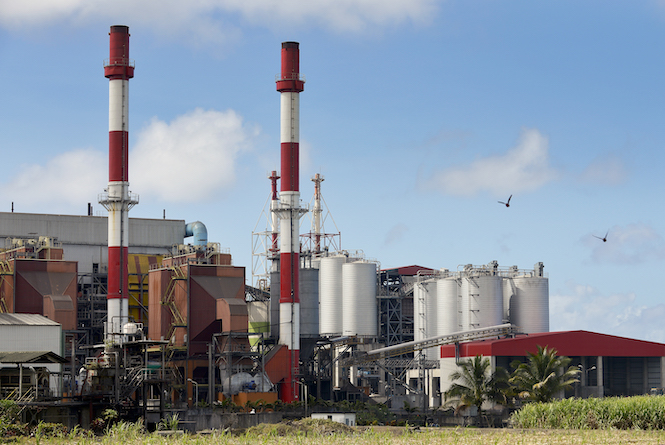
- Type: Thermal biomass power plant
- Installed since: 2007
- Installed capacity: 90 MW
- Workforce: 80
Commissioned in 2007, the Savannah biomass-fuelled thermal power plant produces low-pressure steam electric power for the Mauritian network.
Activities
The cogeneration plant located in Savannah, in southern Mauritius, has an installed capacity of 90 MW. It is jointly owned by the sugar producer OTEO LB, a company including Omnicane, Albioma and the Sugar Investment Trust, an investment cooperative run by Mauritian sugar industry workers.
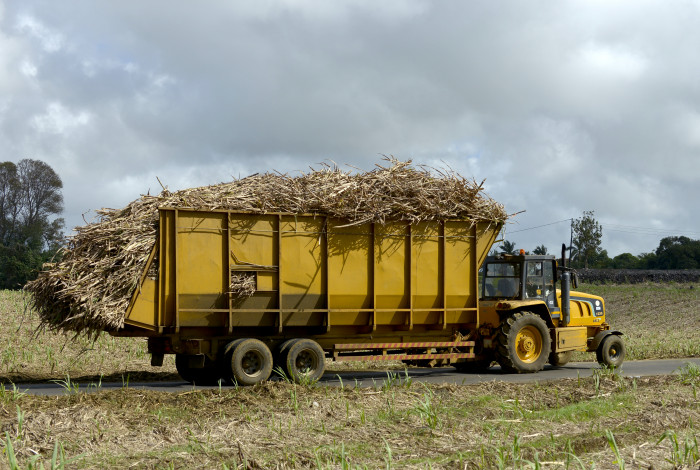
Biomass and energy production
During sugar harvests, the Savannah plant operates essentially using bagasse, simultaneously generating electricity for the Central Electricity Board network and supplying the low-pressure steam required by Omnicane’s sugar refinery. Bagasse is a fibrous resource present in abundance in Mauritius, where sugar cane plantations remain the leading local agricultural resource.
Carbon Burn-Out – A world first
At the Savannah plant in 2016, Omnicane and Albioma commissioned a system to decrease the amount of carbon present in coal waste. In 2019, this world-first “carbon burn-out” technology would used to process almost 40% (by tonnage) of the combustion by-products resulting from the activities at the Savannah, Terragen and Saint-Aubin plants, recovering them for use as cement admixtures in the construction industry.






